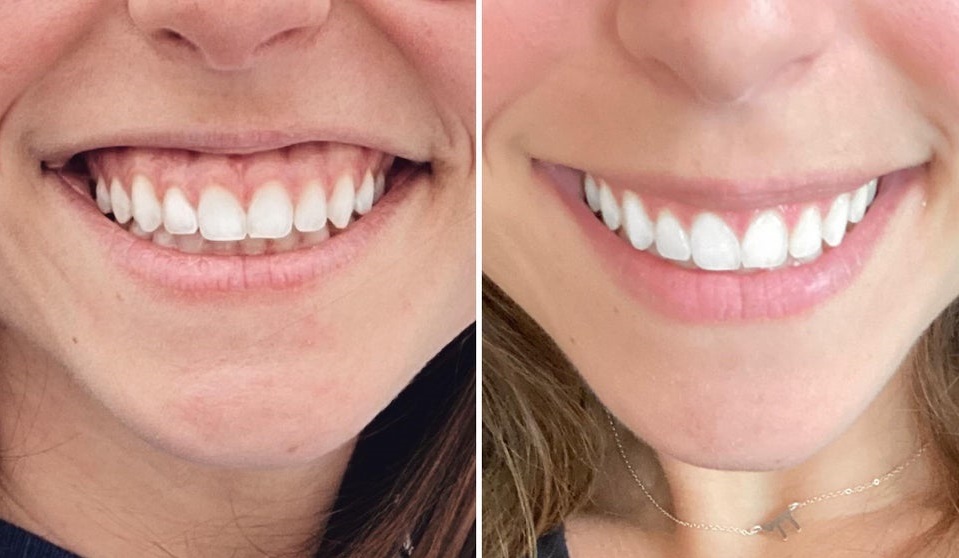
A gummy smile, clinically known as excessive gingival display, occurs when too much gum tissue is visible above the upper teeth when a person smiles, often leading to self-consciousness. While the ideal smile typically exposes about 2 millimeters or less of gum tissue, anything significantly beyond this threshold can draw attention away from the teeth. The good news is that a gummy smile is a common aesthetic concern with highly effective, modern treatment options, ranging from simple, non-surgical solutions like Botox injections to specialized surgical procedures such as gingivectomy (gum contouring) or lip repositioning surgery. The underlying causes of a gummy smile are varied, including genetics, jaw structure, and muscular hyperactivity, necessitating a precise diagnosis by a specialist to determine the best path for smile harmonization.
Smile Too Gummy? Here’s Why
| Underlying Cause | Primary Mechanism | Recommended Treatment Focus | Typical Treatment Type |
| Short Upper Lip | The lip lifts too high due to its short physical length. | Surgical modification to restrict muscle lift. | Lip Repositioning Surgery |
| Hyperactive Lip Muscle | The muscle (levator labii superioris) pulls the lip excessively upwards during a smile. | Muscle relaxation to reduce the hyperactivity. | Botox Injections (non-surgical) |
| Excess Gum Tissue | The gums cover too much of the tooth crown, making teeth look short. | Removal of excess gum and bone tissue. | Gingivectomy / Crown Lengthening |
| Vertical Maxillary Excess (VME) | The upper jaw bone (maxilla) is too long relative to the face. | Skeletal correction to reposition the jaw. | Orthognathic Surgery (Jaw Surgery) |
| Over-Erupted Teeth | The teeth and supporting bone have moved too far down. | Intrusion to push the teeth back into the bone. | Orthodontic Treatment (with or without TADs) |
What is a gummy smile?
A gummy smile, or excessive gingival display (EGD), is an aesthetic condition defined by the display of more than the desirable amount of gum tissue (gingiva) when a person smiles naturally. While beauty is subjective, dental and facial esthetic standards generally suggest that a smile is optimally balanced when 2 to 4 millimeters of gum tissue are visible.
When the amount of visible gum exceeds this range sometimes showing 4mm, 5mm, or even more—it is categorized as a gummy smile. This condition is entirely benign from a functional health perspective but can significantly impact a person’s self-esteem and confidence, prompting many to seek cosmetic correction through gum contouring or other advanced treatments.
Causes of Gummy Smile:
The effective treatment of a gummy smile depends entirely on accurately identifying its specific root cause. The causes can be broadly classified into skeletal, muscular, dental, or gingival factors.
1. Gingival Causes (Excess Gum Tissue)
This is often the simplest cause to fix. The teeth themselves are of normal size, but the gums have failed to fully recede to the correct position after the teeth erupted, covering too much of the natural clinical crown (the visible part of the tooth).
- Treatment Focus: Gingivectomy or Crown Lengthening.
2. Muscular Causes (Hyperactive Lip)
This occurs when the lip muscles are excessively strong or hyperactive, causing the upper lip to rise too high during a smile.
- The muscle responsible is primarily the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi (LLSAN).
- The actual gum and teeth structure may be normal, but the muscular pull exposes too much of the gingiva.
- Treatment Focus: Muscle relaxation via Botox Injections or restricted movement via Lip Repositioning Surgery.
3. Skeletal Causes (Vertical Maxillary Excess – VME)
This is a more complex, structural cause. Vertical Maxillary Excess means the upper jaw bone (maxilla) is vertically too long, causing the entire gum and tooth structure to hang lower than the facial midline dictates.
- This typically results in both a gummy smile and often an overbite.
- Treatment Focus: Skeletal correction using Orthognathic Surgery.
4. Dental Causes (Tooth Wear or Eruption Issues)
Sometimes, the issue is not the gums, but the way the teeth have erupted or been worn down.
- Under-Erupted Teeth: Teeth have not fully emerged from the gums, making them appear too short.
- Over-Eruption: The teeth and their supporting bone have moved too far downwards.
- Treatment Focus: Orthodontic treatment (often involving skeletal anchors) to push the teeth back into the bone.
Treatment Options for Gummy Smile:
Modern dentistry offers a hierarchy of solutions for gummy smile correction, ranging from non-invasive injections to major surgery. The correct choice provides the most predictable and aesthetically pleasing outcome.
Orthodontic treatment:
Orthodontics is a primary solution when the cause is a dental factor, such as the teeth being positioned too far down (over-erupted).
- Mechanism: Specialized braces or clear aligners are used, often in conjunction with temporary anchorage devices (TADs) or mini-screws placed in the bone.
- Goal: To “intrude” (push back up) the upper teeth and the supporting bone segment, effectively shortening the vertical length of the dental structure and reducing gum display.
- Suitability: Excellent for mild to moderate cases where VME is not severe.
Gingivectomy (Gum Contouring):
A Gingivectomy, or gum contouring, is the treatment of choice when the cause is mild-to-moderate excess gum tissue covering the teeth (Gingival Causes).
- Procedure: This minimally invasive procedure uses a scalpel or, more commonly, a soft-tissue dental laser to carefully remove the excess gum tissue, reshaping the gum line to expose the full, natural length of the teeth (the clinical crown).
- Recovery: Quick and involves minimal discomfort.
- Limitation: It only removes soft tissue. If bone tissue needs reduction to prevent the gums from growing back, a more complex procedure called Crown Lengthening is necessary.
Lip repositioning surgery:
This procedure is designed specifically for gummy smiles caused by a hyperactive lip muscle or a short upper lip.
- Procedure: The surgeon makes incisions inside the mouth, beneath the lip, to surgically restrict the movement of the muscles and soft tissues that pull the lip upwards. This effectively lowers the maximum height the lip can achieve when smiling.
- Benefit: Provides a permanent, often dramatic solution for muscular hyperactivity without affecting the bone or teeth.
- Suitability: Highly effective for isolated muscular causes where the teeth and jaw structure are normal.
Botox Injections
Botox offers a simple, non-surgical, and temporary solution for a hyperactive lip muscle (muscular cause).
- Procedure: Small amounts of botulinum toxin are injected into the specific hyperactive muscles responsible for pulling the upper lip too high.
- Mechanism: The Botox temporarily relaxes these muscles, limiting their range of movement and preventing the lip from retracting excessively during a smile, thereby hiding the excessive gum.
- Limitation: The effect is temporary, lasting typically 3 to 6 months, requiring repeat Botox injections for maintenance. It is a great test treatment before committing to permanent surgery.
Crown Lengthening
When excess gum tissue is reinforced by excess bone tissue, a Gingivectomy is insufficient. Crown Lengthening is a surgical procedure that addresses both.
- Procedure: The surgeon not only removes excess gum tissue but also precisely reshapes and removes a small amount of underlying bone (osseous tissue) that supports the gum.
- Goal: This creates a stable, new gum line that will not grow back over the tooth, ensuring long-term aesthetic stability.
- Suitability: Essential for severe gingival excess or when the tooth is needed for restorative procedures (like crowns).
Orthognathic Surgery
For the most severe gummy smile cases rooted in a significant Vertical Maxillary Excess (VME) or malocclusion (bad bite), Orthognathic Surgery (Jaw Surgery) is required.
- Procedure: This major surgical procedure involves physically repositioning the upper jaw (maxilla) upwards within the facial skeleton, correcting the skeletal disproportion and significantly reducing the gum exposure.
- Specialization: Performed by an Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon (OMFS) and often requires pre- and post-surgical orthodontic treatment.
- Benefit: Provides the most complete and stable correction for severe skeletal issues, often correcting underlying functional bite problems simultaneously.
Factors to Consider Before Treatment
Before committing to any gummy smile correction procedure, patients must undergo a thorough evaluation and consider several factors:
- Accurate Diagnosis: The most critical step is determining the exact cause (muscular, skeletal, or gingival) as this dictates the success of the treatment. A specialist should use clinical assessment and detailed radiographic analysis.
- Treatment Longevity: Evaluate whether you prefer a permanent solution (Crown Lengthening, Lip Repositioning) or a temporary, non-invasive one (Botox Injections).
- Recovery Time and Invasiveness: Gingivectomy offers a short recovery, while Orthognathic Surgery requires significant downtime.
- Cost: Non-surgical options are highly affordable but require recurrence; surgical options are a higher one-time investment.
Eligibility Criteria for Gummy Smile Surgery
Eligibility is determined on a case-by-case basis, but general criteria include:
- Good General Health: Required for all surgical procedures.
- Sufficient Tooth Length: For Gingivectomy or Crown Lengthening, the buried portion of the tooth must be long enough to expose a naturally sized tooth without compromising bone support.
- Skeletal Maturity: Orthognathic Surgery is typically reserved for adults whose facial and jaw growth is complete.
- Realistic Expectations: Patients must understand the potential aesthetic limits and recovery process associated with the chosen surgical path.
Conclusion
The gummy smile is no longer a condition patients must simply live with. With modern advancements in aesthetic dentistry and oral surgery, there are safe, predictable, and effective treatment options available for every underlying cause. Whether you choose the minimal invasiveness of Botox injections for muscle relaxation or the definitive results of Crown Lengthening or Lip Repositioning Surgery, consultation with a specialized professional is the essential first step towards achieving a perfectly balanced and confident smile.
Would you like me to focus on the ideal recovery timeline for the three most common procedures: Botox, Gingivectomy, and Lip Repositioning Surgery?